The weekly litigation news digest is live. Subscribe now
Method Of Modifying Eukaryotic Cells - EP3085779
The patent EP3085779 was granted to Regeneron Pharmaceuticals on May 31, 2023. The application was filed on Feb 15, 2002 under application number EP16171559A. The patent is currently recorded with a legal status of "Patent Maintained As Amended".
EP3085779
- Application Number
- EP16171559A
- Filing Date
- Feb 15, 2002
- Status
- Patent Maintained As Amended
- Apr 28, 2023
- Publication Date
- May 31, 2023
- External Links
- Slate, Register, Google Patents
Patent Summary
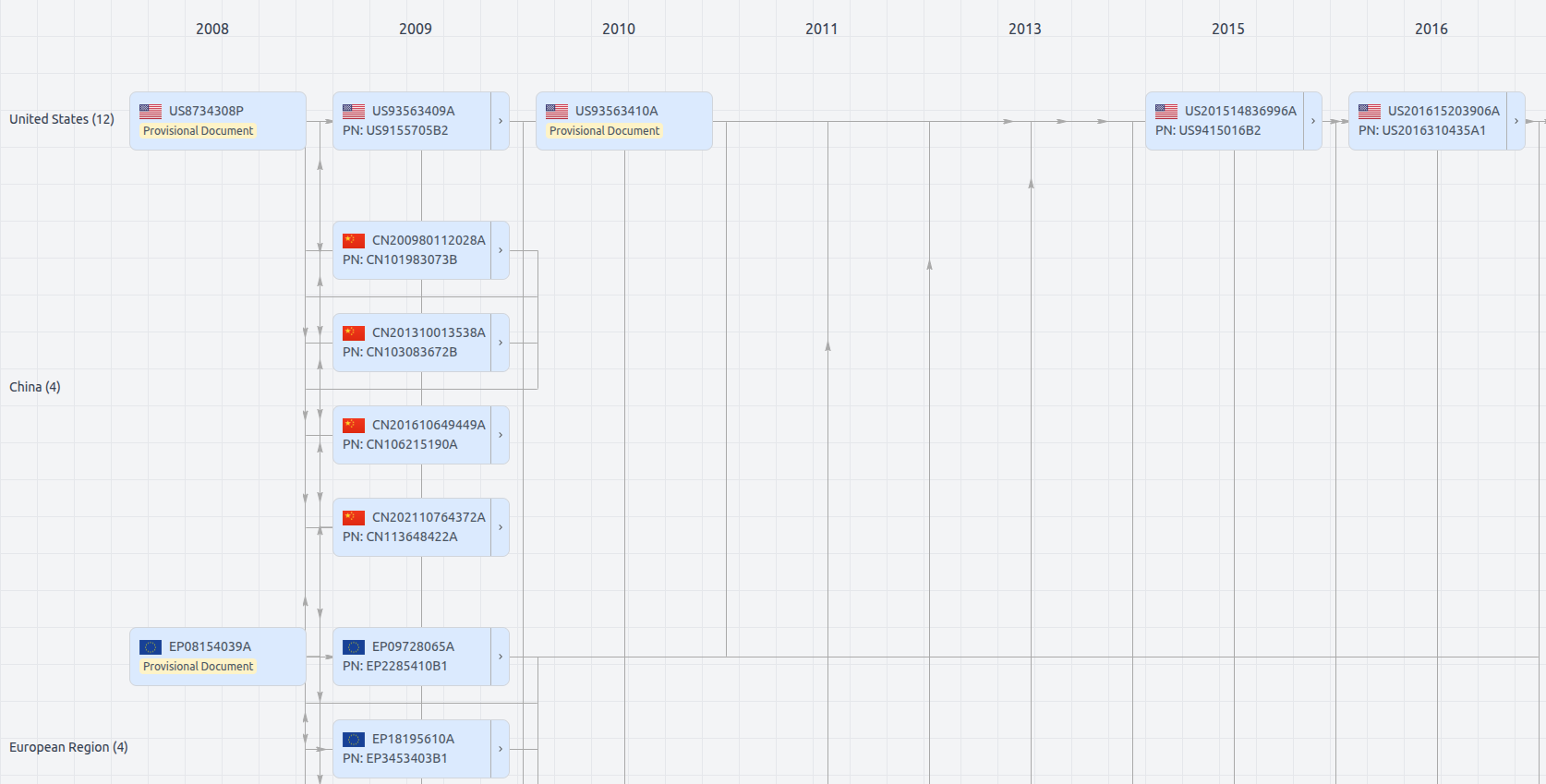
Patent Family
Patent Oppositions
Patent oppositions filed by competitors challenge the validity of a granted patent. These oppositions are typically based on claims of prior art, lack of novelty, or non-obviousness. They are a key part of the process for determining a patent's strength and enforceability.
| Company | Opposition Date | Representative | Opposition Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| KYMAB | Apr 5, 2019 | CMS CAMERON MCKENNA NABARRO OLSWANG | WITHDRAWN |
Patent Citations (28) New
Patent citations refer to prior patents cited during different phases such as opposition or international search.
| Citation Phase | Publication Number |
|---|---|
| DESCRIPTION | US5350689 |
| DESCRIPTION | US5436149 |
| DESCRIPTION | US5508189 |
| DESCRIPTION | US5770429 |
| DESCRIPTION | US5789215 |
| EXAMINATION | US6069010 |
| OPPOSITION | EP1204740 |
| OPPOSITION | EP1360287 |
| OPPOSITION | EP1399575 |
| OPPOSITION | EP2264163 |
| OPPOSITION | EP2786657 |
| OPPOSITION | EP2787075 |
| OPPOSITION | EP3028564 |
| OPPOSITION | US2007280945 |
| OPPOSITION | US5789215 |
| OPPOSITION | US6114598 |
| OPPOSITION | US9012717 |
| OPPOSITION | WO0236789 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2008054606 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2008076379 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2009018411 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2009023540 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2015088643 |
| OPPOSITION | WO2016081923 |
| OPPOSITION | WO9100906 |
| OPPOSITION | WO9945962 |
| SEARCH | US5939598 |
| SEARCH | WO9945962 |
Dossier Documents
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
May 8, 2023
Apr 28, 2023
Apr 18, 2023
Apr 18, 2023
Apr 18, 2023
Apr 18, 2023
Apr 18, 2023
Apr 3, 2023
Jan 17, 2023
Jan 17, 2023
Jan 17, 2023
Jan 17, 2023
Jan 17, 2023
Nov 17, 2022
Nov 17, 2022
Nov 16, 2022
Refund of fees
Appeal
Nov 14, 2022
Nov 14, 2022
Nov 14, 2022
Nov 9, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Nov 9, 2022
Nov 9, 2022
Refund of fees
Appeal
Nov 9, 2022
Withdrawal of an appeal
Appeal
Nov 4, 2022
Nov 4, 2022
Nov 3, 2022
Oct 31, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Oct 31, 2022
Oct 31, 2022
Oct 28, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Oct 28, 2022
Oct 28, 2022
Withdrawal of an appeal
Appeal
May 23, 2022
May 20, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
May 20, 2022
May 20, 2022
May 20, 2022
May 20, 2022
May 20, 2022
May 20, 2022
Reply to appeal
Appeal
May 19, 2022
May 18, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
May 18, 2022
May 18, 2022
Reply to appeal
Appeal
May 13, 2022
Jan 13, 2022
Jan 13, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 10, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Jan 7, 2022
Nov 15, 2021
Nov 15, 2021
Nov 8, 2021
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Nov 8, 2021
Nov 8, 2021
Notice of appeal
Appeal
Nov 3, 2021
(Electronic) Receipt
Appeal
Nov 3, 2021
Nov 3, 2021
Notice of appeal
Appeal
Sep 3, 2021
Sep 3, 2021
Sep 3, 2021
Sep 1, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Means of redress
OPPO
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Aug 30, 2021
Jun 23, 2021
Jun 22, 2021
Jun 16, 2021
Jun 16, 2021
Jun 16, 2021
May 20, 2021
May 14, 2021
May 14, 2021
May 14, 2021
Apr 30, 2021
Apr 29, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 23, 2021
Apr 12, 2021
Apr 6, 2021
Apr 6, 2021
Apr 6, 2021
Mar 22, 2021
Mar 22, 2021
Mar 17, 2021
Mar 11, 2021
Mar 11, 2021
Mar 11, 2021
Feb 23, 2021
Feb 23, 2021
Nov 9, 2020
Nov 6, 2020
Nov 6, 2020
Nov 6, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Nov 2, 2020
Sep 17, 2020
Sep 9, 2020
Sep 9, 2020
Sep 9, 2020
Jul 16, 2020
Jul 10, 2020
Jul 10, 2020
Jul 10, 2020
Jul 10, 2020
Jun 12, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Jun 5, 2020
Feb 12, 2020
Jan 30, 2020
Jan 30, 2020
Jan 28, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 17, 2020
Jan 16, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Jan 3, 2020
Apr 15, 2019
Apr 12, 2019
Apr 5, 2019
Apr 5, 2019
Apr 5, 2019
Mar 7, 2019
Decision to grant a European patent
Search/Exam
Feb 19, 2019
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Feb 19, 2019
Filing of the translations of the claims
Search/Exam
Feb 19, 2019
French translation of claims
Search/Exam
Feb 19, 2019
German translation of the claims
Search/Exam
Feb 19, 2019
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2019
Feb 13, 2019
Feb 13, 2019
Feb 13, 2019
Intention to grant (signatures)
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2019
Text intended for grant (clean copy)
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2019
Text intended for grant (sequence listing)
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2019
Jan 23, 2019
Jan 23, 2019
Jan 23, 2019
Intention to grant (signatures)
Search/Exam
Jan 23, 2019
Text intended for grant (clean copy)
Search/Exam
Jan 23, 2019
Text intended for grant (sequence listing)
Search/Exam
Jan 23, 2019
Aug 30, 2018
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Aug 30, 2018
Description
Search/Exam
Aug 30, 2018
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Aug 30, 2018
Aug 27, 2018
Annex to the communication
Search/Exam
Aug 27, 2018
Consultation by telephone/in person
Search/Exam
Aug 27, 2018
Aug 7, 2018
Annex to the communication
Search/Exam
Aug 7, 2018
Communication from the Examining Division
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Amended claims with annotations
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Amended description with annotations
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Claims
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Description
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Mar 26, 2018
Nov 27, 2017
Annex to the communication
Search/Exam
Nov 27, 2017
Communication from the Examining Division
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Amended claims with annotations
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Amended description with annotations
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Claims
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Description
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Jul 12, 2017
Jun 12, 2017
Annex to the communication
Search/Exam
Jun 12, 2017
Communication from the Examining Division
Search/Exam
Jun 12, 2017
Jun 7, 2017
Jun 6, 2017
Feb 13, 2017
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Amended claims with annotations
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Amended description with annotations
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Claims
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Description
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Feb 13, 2017
Jan 4, 2017
Annex to the communication
Search/Exam
Jan 4, 2017
Communication from the Examining Division
Search/Exam
Oct 31, 2016
Sep 28, 2016
Notification of forthcoming publication
Search/Exam
Sep 26, 2016
(Electronic) Receipt
Search/Exam
Sep 26, 2016
Sep 26, 2016
Amended claims with annotations
Search/Exam
Sep 26, 2016
Amendments received before examination
Search/Exam
Sep 26, 2016
Letter accompanying subsequently filed items
Search/Exam
Jul 27, 2016
Refund of fees
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 19, 2016
Communication to designated inventor
Search/Exam
Jul 18, 2016
Jul 18, 2016
European search opinion
Search/Exam
Jul 18, 2016
European search report
Search/Exam
Jul 18, 2016
Information on Search Strategy
Search/Exam
Jul 8, 2016
Search started
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Abstract
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
May 26, 2016
Claims
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Converted Sequence Listing
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Description
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Designation of inventor
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Drawings
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Letter concerning search matters
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Matter concerning the application
Search/Exam
May 26, 2016
Request for grant of a European patent
Search/Exam
Sep 12, 2002