Semiconductor Source Based Near Infrared Measurement Device With Improved Signal-To-Noise Ratio
Patent No. US10874304 (titled "Semiconductor Source Based Near Infrared Measurement Device With Improved Signal-To-Noise Ratio") was filed by Omni Medsci Inc on Oct 31, 2019.
What is this patent about?
’304 is related to the field of lasers and light sources for healthcare, medical, dental, or bio-technology applications. More specifically, it concerns systems and methods for using near-infrared or short-wave infrared light sources for early detection of dental caries. Traditional methods for caries detection, such as visual examination and x-ray imaging, can be subjective and may not detect early-stage lesions effectively. Current imaging methods based on light transport changes within the tooth, like fiber-optic trans-illumination and quantitative light-induced fluorescence (QLF), have limitations in quantification, contrast, and discrimination between caries and stains.
The underlying idea behind ’304 is to improve the signal-to-noise ratio in optical measurements of blood constituents by increasing the light intensity from semiconductor sources in the near-infrared spectrum. This increased intensity helps overcome challenges posed by interfering spectral features from other blood constituents and the skin. The system also captures light when the light source is off and subtracts this from the signal when the light source is on, further reducing noise.
The claims of ’304 focus on a measurement system comprising a light source with multiple semiconductor sources, a measurement device, a receiver, a smartphone or tablet, and a cloud. The light source is configured to generate an output optical beam with one or more optical wavelengths and to increase signal-to-noise ratio by increasing light intensity. The receiver is configured to receive and process reflected or transmitted light from a sample, generate an output signal representing a non-invasive measurement on blood, synchronize to the light source, and improve the signal-to-noise ratio by differencing signals captured when the light source is on and off .
In practice, the system works by modulating the light source and synchronizing the receiver to this modulation, using a lock-in technique to detect the modulation frequency and reject noise. The receiver also captures light while the light source is off and subtracts this from the signal when the light source is on, further reducing noise. The smartphone or tablet processes, stores, and displays the output signal and transmits it to the cloud, which processes and stores the data. This allows for remote monitoring and analysis of the data by healthcare providers.
This approach differs from prior solutions by using a combination of increased light intensity and signal differencing to improve signal-to-noise ratio. Prior art methods often rely on weaker light sources or do not effectively account for background noise and interfering signals. By using a smartphone and cloud connectivity, the system also enables remote monitoring and data analysis, which is not typically found in traditional caries detection methods. The use of multiple semiconductor sources allows for a broader spectrum of light to be used, which can improve the accuracy of the measurements.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the early 2010s when ’304 was filed, non-invasive physiological measurements using near-infrared spectroscopy were gaining traction, at a time when signal processing techniques were commonly relied upon to improve the signal-to-noise ratio in such measurements. Wearable devices were also becoming more prevalent, but hardware and software constraints made it non-trivial to integrate complex signal processing and data analysis capabilities directly into the device itself.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because the prior art, whether considered individually or in combination, did not disclose the specific claimed features. These features include generating an output signal representing a non-invasive measurement on blood, synchronizing to the light source, capturing light while the semiconductor sources are off and converting it into a first signal.
Claims
This patent contains 27 claims, with claims 1, 11, and 19 being independent. The independent claims are directed to measurement systems and wearable devices that use a light source with multiple semiconductor sources to perform non-invasive measurements, particularly on blood, and involve processing and transmitting data to a smartphone/tablet and a cloud. The dependent claims generally elaborate on specific components, configurations, and functionalities of the measurement systems and wearable devices described in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
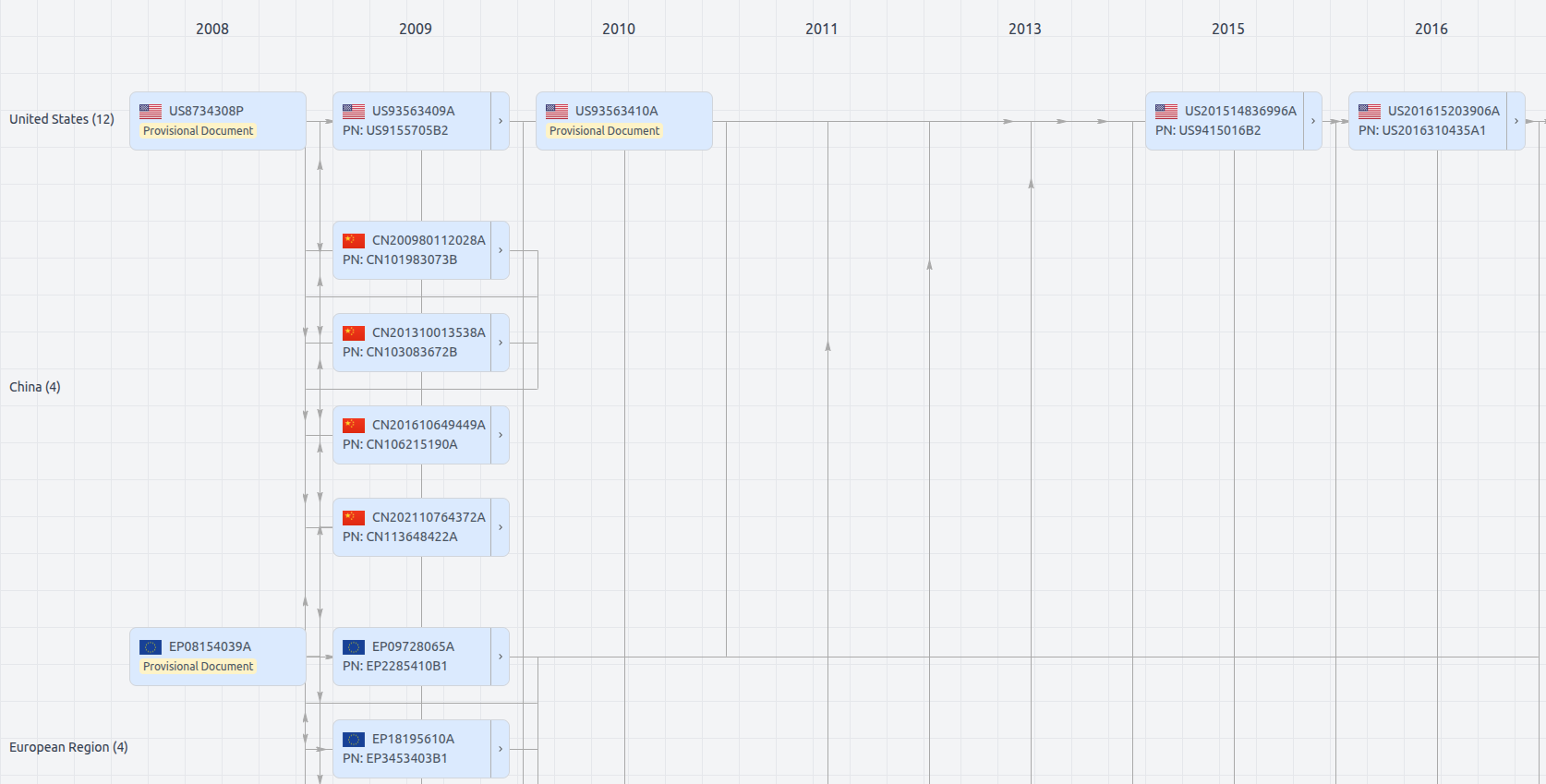
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Get instant alerts for new documents
US10874304
- Application Number
- US16669794
- Filing Date
- Oct 31, 2019
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Dec 17, 2033
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents