Validating Automatic Number Identification Data
Patent No. US11005989 (titled "Validating Automatic Number Identification Data") was filed by Rightquestion Llc on Feb 7, 2020.
What is this patent about?
’989 is related to the field of telecommunications security, specifically addressing the problem of caller ID spoofing. Traditional caller ID systems are vulnerable to manipulation, making it difficult to trust the displayed number. This creates opportunities for fraud and necessitates resource-intensive verification processes for organizations like customer support centers.
The underlying idea behind ’989 is to establish a more reliable method for verifying caller identification by using a secondary communication channel to confirm the association between a calling device and its claimed phone number. This involves sending a challenge to the device via a separate channel (e.g., SMS, data connection) and validating the response, thereby increasing confidence in the caller's identity.
The claims of ’989 focus on receiving information about a call, including a value derived from the calling device and a validity score for the phone number. A security determination is made based on both the score and verification of the device-derived value. Finally, based on this determination, either assurance or failure to confirm is communicated to the call recipient.
In practice, the system relies on a client-side agent (e.g., an app) on the calling device. When a call is initiated, the agent generates a message containing device-specific information and transmits it to a verification service. The verification service then correlates this information with the call details received by the callee, making a security determination that is relayed back to the callee for a policy-based decision.
This approach differentiates itself from prior art by employing a multi-factor verification process. Instead of solely relying on the caller ID presented during the call setup, it incorporates a device-generated value and a validity score, enhancing the accuracy and robustness of the verification process. The use of a secondary channel for verification further mitigates the risk of spoofing attacks that might compromise the primary call setup channel.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the early 2010s when ’989 was filed, mobile communication systems commonly relied on SMS for text messaging and voice calls, at a time when caller ID spoofing was a known problem. Systems commonly relied on ANI data for caller identification, but hardware or software constraints made robust validation of this data non-trivial.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because they agreed that the prior art of record does not teach the independent claims 2, 21, and 22. Claims 3-5 and 8-31 were allowed as depending from claim 2.
Claims
This patent contains 28 claims, with independent claims 1, 27, and 28. The independent claims are focused on a system, a method, and a computer program product for performing a security determination on a call based on a score and a value associated with the calling device, and then conveying an assurance or failure to confirm to the callee. The dependent claims generally elaborate on and provide specific details and implementations of the elements and steps recited in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Patent Family
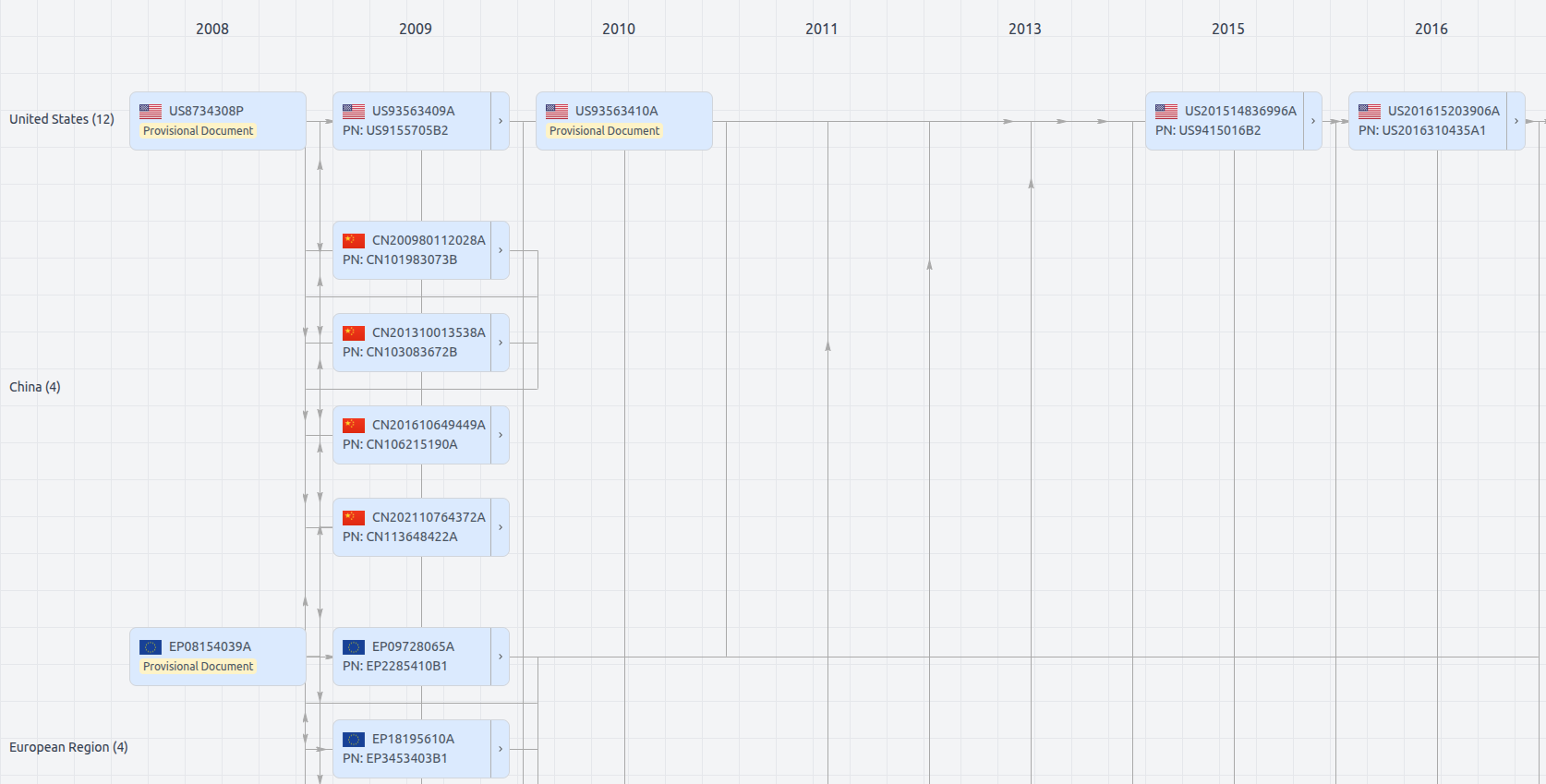
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11005989
- Application Number
- US16785423
- Filing Date
- Feb 7, 2020
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Nov 6, 2034
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents