Modification Of Terminal And Service Provider Machines Using An Update Server Machine
Patent No. US11210082 (titled "Modification Of Terminal And Service Provider Machines Using An Update Server Machine") was filed by S3G Technology Llc on Sep 25, 2020.
What is this patent about?
’082 is related to the field of computerized systems and, more specifically, to the modification of software on remote devices. The background involves systems where software applications on multiple devices interact, such as a terminal used by a customer and a server used by a service provider. Updating these applications, especially over networks with limited bandwidth, poses a challenge because transmitting entire new software versions is often impractical.
The underlying idea behind ’082 is to enable efficient modification of software applications distributed across a network by updating only the dialogue modules that define the interaction between devices. Instead of sending entire application updates, the system sends smaller code updates that modify the application's behavior without requiring recompilation of the core application logic. This is achieved by using a platform module that interprets the dialogue module code.
The claims of ’082 focus on a method and system for conducting a dialogue sequence using a service provider machine. The service provider machine has a provider application with computer-executable instructions and code. The code is updated by receiving new code that either replaces or supplements the existing code. This updated code adapts the provider application to conduct a modified dialogue sequence. The service provider machine then sends code to a recipient to facilitate the recipient's portion of the modified dialogue sequence.
In practice, the system involves an update server that sends dialogue modules to both a terminal machine and a service provider machine. These modules contain code that modifies the behavior of the applications running on each machine, adapting the dialogue protocol between them. The dialogue modules are smaller than full application updates, making them suitable for transmission over networks with limited bandwidth. The core application logic, written in computer-executable instructions, remains unchanged, while the dialogue modules, containing code that needs translation, are updated to modify the interaction flow.
This approach differs from traditional software updates where entire applications are recompiled and redistributed. By focusing on updating only the dialogue modules, the system achieves efficient modification of software applications, especially in scenarios where devices are distributed across a network and bandwidth is limited. The use of a platform module to interpret the dialogue module code allows for dynamic adaptation of the application's behavior without requiring recompilation of the core application logic, enabling rapid customization and updates to the dialogue protocol.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2000s when ’082 was filed, software distribution to remote devices over networks with limited bandwidth was a significant challenge. At a time when software updates were typically implemented using full application replacements, transmitting large amounts of data over wireless networks was often economically infeasible and time-consuming. When systems commonly relied on monolithic application architectures, modifying specific functionalities required redistributing the entire application, making targeted updates non-trivial.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner allowed the claims because they include limitations not found in the prior art. Specifically, the claims recite storing a portion of information associated with data entry, receiving code to replace or supplement the provider application code to adapt the application for a modified dialogue sequence, where the code must be translated before execution, and sending code to facilitate the recipient's portion of the modified dialogue sequence, also requiring translation before execution.
Claims
This patent contains 20 claims, with independent claims 1, 19, and 20. The independent claims are generally directed to a method, a service provider machine, and a computer network, respectively, all configured for conducting a dialogue sequence with code updates. The dependent claims generally elaborate on and refine the elements and steps recited in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
Patent Family
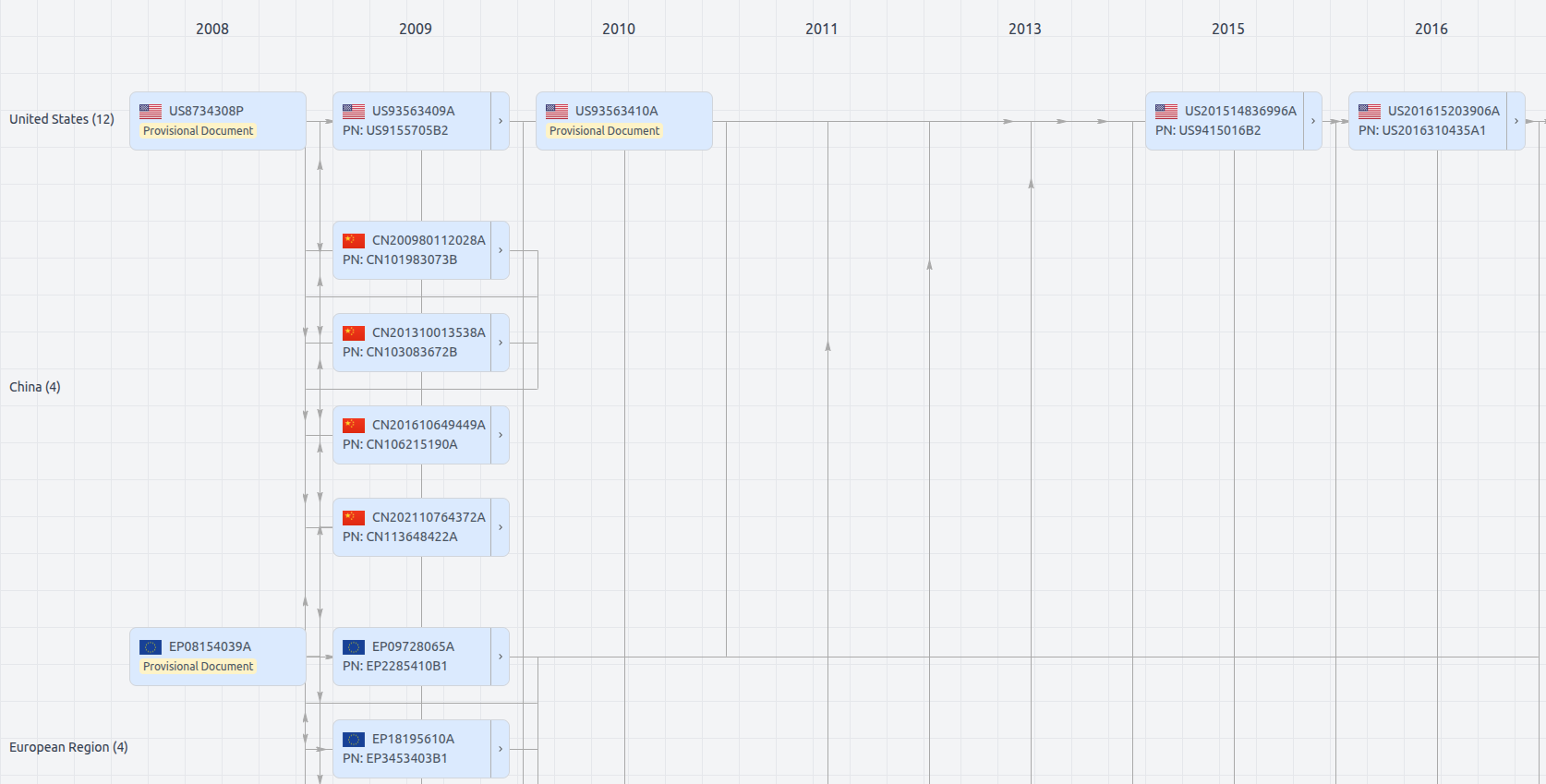
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11210082
- Application Number
- US17033633
- Filing Date
- Sep 25, 2020
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Jul 21, 2030
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents