Backrest Locking Mechanism And Child Safety Seat Therewith
Patent No. US11318866 (titled "Backrest Locking Mechanism And Child Safety Seat Therewith") was filed by Wonderland Switzerland Ag on Sep 22, 2020.
What is this patent about?
’866 is related to the field of child safety seats, specifically focusing on mechanisms that allow for the detachable connection of a backrest to the base of the seat. The background acknowledges the need for easy packaging, transportation, and storage of child safety seats, which necessitates a detachable backrest. Existing locking mechanisms are criticized for being complex and not user-friendly, creating a need for a simpler and more convenient solution.
The underlying idea behind ’866 is to provide a simplified locking mechanism for a child safety seat backrest that allows for easy and convenient attachment and detachment. This is achieved by using a locking pin on either the backrest or the base, a locking component with a hole on the other part, and an operating component that moves to engage or disengage the pin from the hole. The operating component provides a user-friendly way to secure or release the backrest.
The claims of ’866 focus on a backrest locking mechanism adapted for a backrest and a base of a child safety seat, where the backrest is detachably connected to the base and includes at least one mounting arm protruding from a lower end of the backrest, and at least one guiding slot being formed on the base. The mounting arm is at least partially accommodated inside the guiding slot and slidable relative to it. The mechanism includes a locking pin on the mounting arm, a locking component with a hole on the base, and an operating component that moves to engage or disengage the pin from the hole.
In practice, the backrest is attached to the base by sliding the mounting arms into the guiding slots. As the mounting arms slide in, the locking pins engage with the locking hole structures on the locking components, securing the backrest. To detach the backrest, the user operates the operating component, which could be a slider, button, or rotating element. This movement disengages the locking pins from the locking hole structures, allowing the backrest to be lifted off the base. A spring or similar element returns the mechanism to the locked position when released.
The key differentiation from prior approaches lies in the simplicity and ease of use of the locking mechanism. By using a direct mechanical linkage between the operating component, locking pin, and locking hole structure, the design avoids complex linkages or intricate mechanisms. The use of a sliding, pressing, or rotating operating component provides a user-friendly interface for quickly and easily attaching or detaching the backrest, addressing the shortcomings of existing, more complicated designs.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2010s when ’866 was filed, child safety seats at a time when backrests were typically implemented to be detachable from the base using locking mechanisms. These mechanisms commonly relied on mechanical components to secure the backrest to the base, when hardware or software constraints made complex electronic locking systems non-trivial.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The claims were rejected under 35 U.S.C. 112(b) or 35 U.S.C. 112 (pre-AIA), second paragraph, as being indefinite for failing to particularly point out and distinctly claim the subject matter which the inventor or a joint inventor regards as the invention. Claims 1-6, 11, and 13 are rejected under 35 U.S.C. 102(a)(1) as being anticipated by Chen (U.S. Patent application Publication No. 2010/0060055 A1). The prosecution record does NOT describe the technical reasoning or specific claim changes that led to allowance.
Claims
The patent has 17 claims, with independent claims 1 and 13. These independent claims are directed to a backrest locking mechanism for a child safety seat and the child safety seat itself. The dependent claims elaborate on specific features and configurations of the locking mechanism and the child safety seat.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
Patent Family
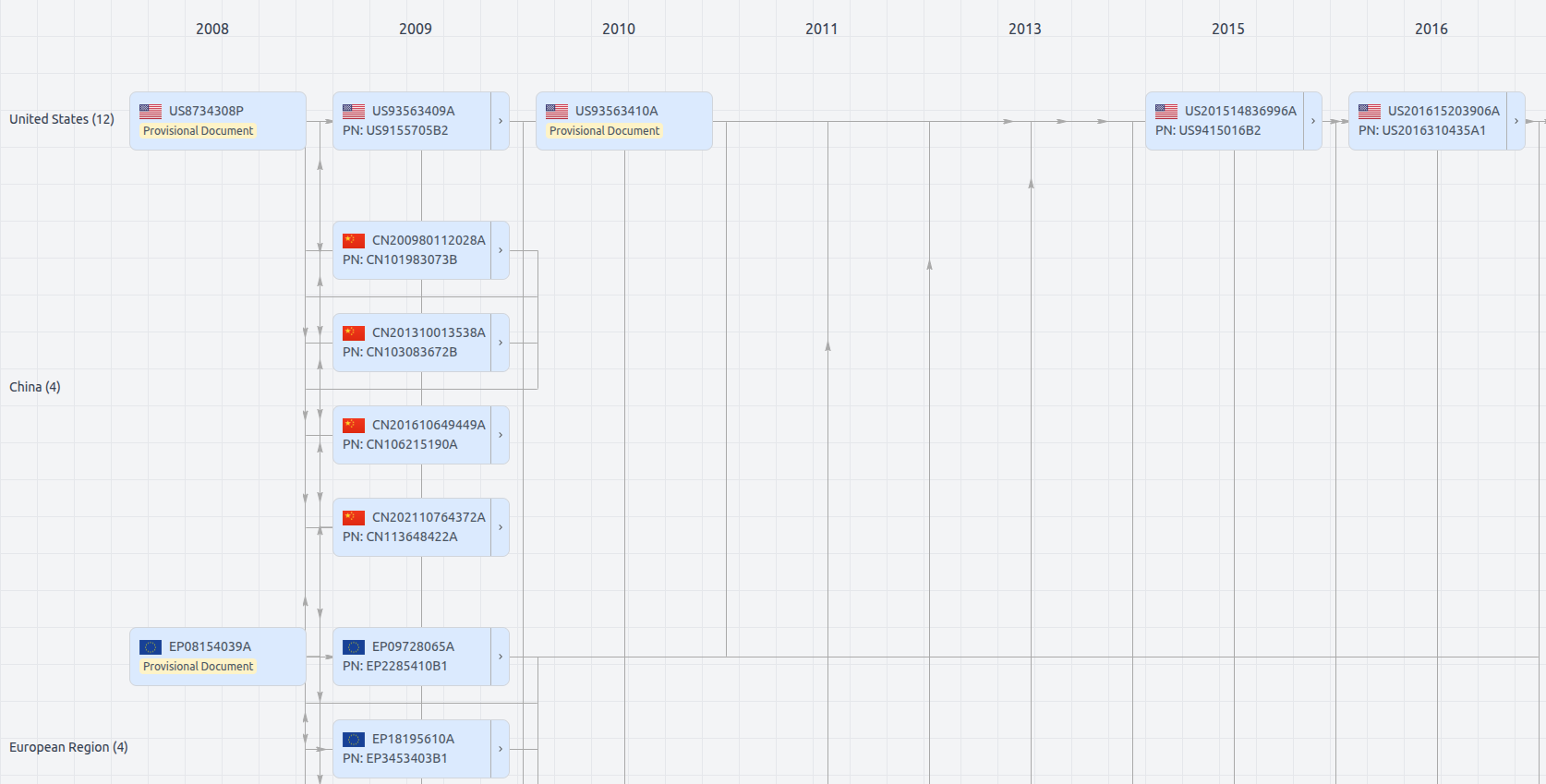
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11318866
- Application Number
- US17028992
- Filing Date
- Sep 22, 2020
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Sep 22, 2040
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents