Control Apparatus
Patent No. US11375254 (titled "Control Apparatus") was filed by Fec Ip Llc on Mar 6, 2017.
What is this patent about?
’254 is related to the field of controlling content playback, specifically in a networked environment. The background involves systems like DLNA, where a media controller (DMC) manages content playback on a renderer (DMR) from a server (DMS). A common problem is efficiently skipping unwanted segments, such as commercials, within video content streamed over a network.
The underlying idea behind ’254 is to have a control apparatus (DMC) analyze the content itself to determine optimal playback positions, and then instruct the playback device (DMR) to jump to those positions. This avoids burdening the server (DMS) with complex analysis or requiring high processing power on the playback device.
The claims of ’254 focus on a control apparatus connected to a content server and a playback device. The apparatus receives content, analyzes it to find chapter positions, determines a first playback position based on these chapters, and then transmits information about this playback position to the playback device. The analysis is performed in parallel with the playback device receiving content directly from the server.
In practice, the control apparatus downloads the video content and analyzes the video and/or audio to detect segments of interest, such as commercials. It then marks the beginning and end of these segments as 'chapters'. When the playback device reaches the start of a marked segment, the control apparatus instructs it to jump to the end, effectively skipping the segment. The control apparatus also sends a content request to the server to send the content to the control apparatus in response to transmitting a playback instruction to the playback device to play the content at the playback device. The control apparatus receives the content from the server device in parallel to the playback device receiving the content from the server device without going through the control apparatus in response to the playback instruction from the control apparatus.
This approach differs from prior solutions by performing the content analysis and playback position determination within the control apparatus itself, rather than relying on the server or playback device. This allows for more flexible and efficient control, especially in scenarios where the server is a simple storage device or the playback device has limited processing capabilities. The parallel processing of content analysis and playback further enhances efficiency.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the mid-2010s when ’254 was filed, content playback systems commonly relied on a digital media server (DMS), a digital media controller (DMC), and a digital media renderer (DMR). At a time when video content was typically distributed over a communications network, hardware or software constraints made efficient control of playback non-trivial.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner allowed the claims because they contain a unique combination of steps for a control device managing content playback on a playback device. This includes a server sending content to the control device upon initiation of playback, the playback device receiving content directly from the server, the control device analyzing the received content to determine chapter positions, displaying images corresponding to those positions, determining a playback position based on user selection of an image, and sending that position to the playback device based on the control device receiving information about the current playback position. The examiner stated that no prior art discloses or renders obvious this combination of features in a content distribution environment.
Claims
This patent contains 20 claims, with claims 1 and 2 being independent. The independent claims are directed to a control apparatus that manages content playback on a playback device by analyzing video and/or audio to determine chapter positions and control playback positions. The dependent claims generally elaborate on specific features, functionalities, and configurations of the control apparatus described in the independent claims, such as user input methods, distributed processing, content synchronization, and DLNA compliance.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Patent Family
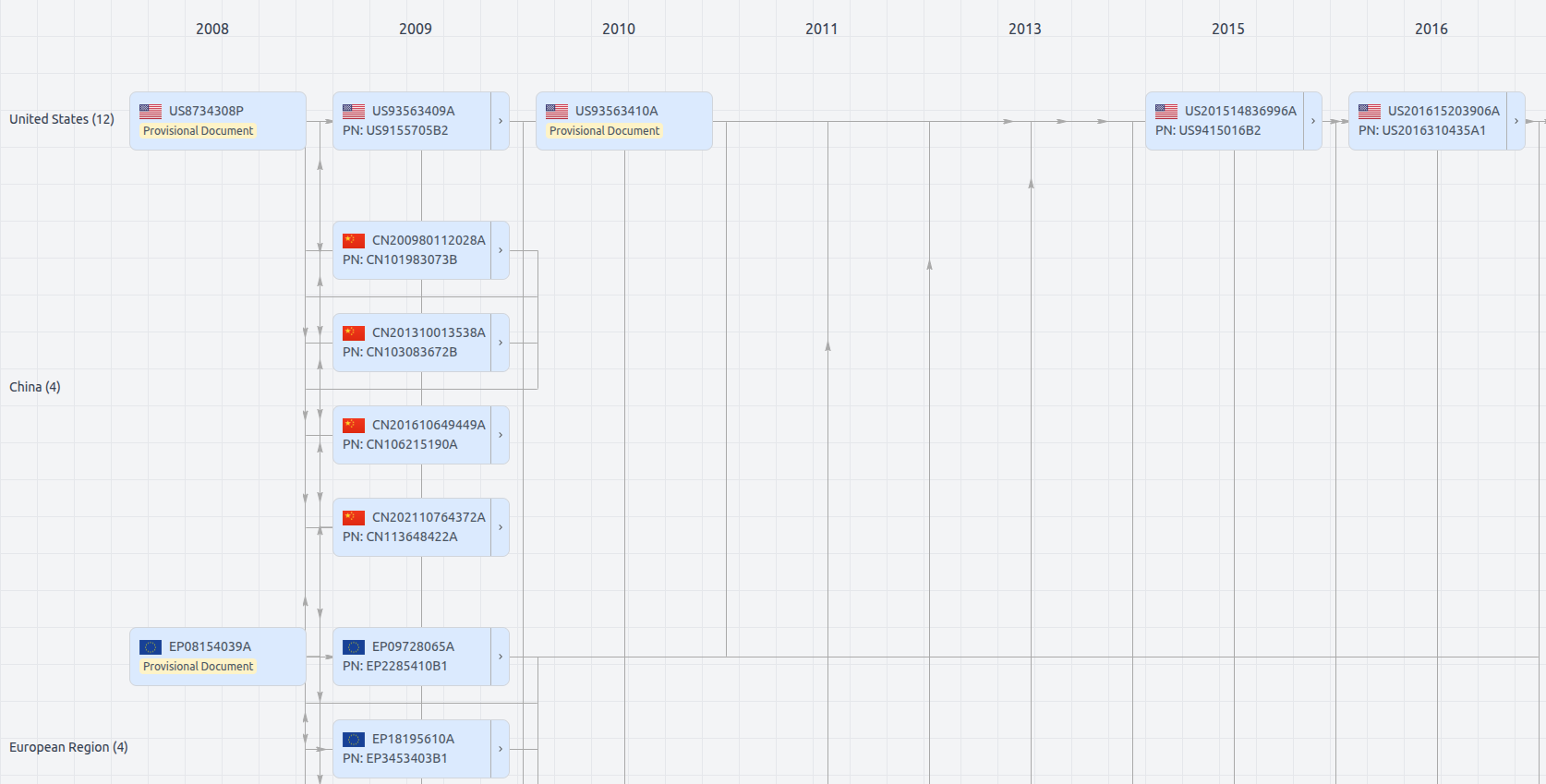
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11375254
- Application Number
- US15450703
- Filing Date
- Mar 6, 2017
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Mar 6, 2037
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents