Strobe-Offset Control Circuit
Patent No. US11551743 (titled "Strobe-Offset Control Circuit") was filed by K.Mizra Llc on Jul 28, 2020.
What is this patent about?
’743 is related to the field of high-speed memory interfaces, specifically addressing the challenge of timing variations between data signals and strobe signals in strobe-based memory systems like DDR SDRAM. These systems rely on a strobe signal (DQS) to capture data (DQ) sent by the DRAM, but system and pin-to-pin offsets can cause timing misalignments, degrading performance. Prior solutions involved manual adjustments or complex timing-calibrated systems, both with drawbacks.
The underlying idea behind ’743 is to implement a per-pin strobe-offset control system that automatically calibrates the timing offset between each data line (DQ) and its corresponding strobe signal (DQS). This is achieved by using a calibration mode where the receiver acts as a phase detector, forming a delay-locked loop (DLL) that adjusts the phase relationship between the strobe and data signals for each bit. The optimal delay value is then maintained in a receiver mode to optimize timing margins during data transfer.
The claims of ’743 focus on an integrated circuit (IC) memory controller that includes command generation circuitry to issue a calibration read command, receiver circuitry to receive calibration read data and an accompanying strobe signal, and phase adjustment circuitry. Crucially, the phase adjustment circuitry adjusts the phase alignment between the strobe signal and the read data based on a first control signal derived from a comparison of the received data pattern during the calibration read operation.
In practice, the system operates in two modes: calibration and receiver. During calibration, a dummy read is performed, and the receiver compares the phase of the data and strobe signals. A calibration control circuit then adjusts a variable delay element to align the strobe signal with the data signal for each pin. Once calibrated, the system switches to receiver mode, where the determined delay is applied to the strobe signal to generate a sample signal used to capture the incoming data, effectively removing unwanted offsets.
This approach differs from prior solutions by providing a simpler, more automated way to compensate for timing variations in strobe-based memory systems. Instead of relying on manual adjustments or complex timing calibration, ’743 uses a DLL-like circuit to dynamically adjust the strobe timing for each data bit, maximizing timing margins and enabling higher-speed data transfer. The system can also store calibration data for use in write operations or to predict offset values for future calibrations.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the mid-2000s when ’743 was filed, at a time when high-speed memory systems commonly relied on strobe-based methods for data transfer, timing variations between data and strobe signals posed a significant challenge. Calibrating timing offsets on a per-pin basis to minimize these variations was desirable but made B non-trivial due to hardware or software constraints.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because the prior art does not teach an integrated circuit memory controller, a method of operation in an integrated circuit memory controller, or an integrated circuit chip that includes command generation circuitry to issue a calibration read command for a calibration read operation and phase adjustment circuitry coupled to the receiver circuitry. The phase adjustment circuitry is operative during the calibration read operation to adjust a phase alignment between the strobe signal and the read data in response to a first control signal.
Claims
This patent contains 14 claims, of which claims 1, 6, and 11 are independent. The independent claims are directed to an integrated circuit memory controller, a method of operation in an integrated circuit memory controller, and an integrated circuit chip, respectively, all generally relating to calibration read operations and phase alignment between a strobe signal and read data. The dependent claims generally elaborate on the features and functionalities described in the independent claims, providing more specific details and implementations.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
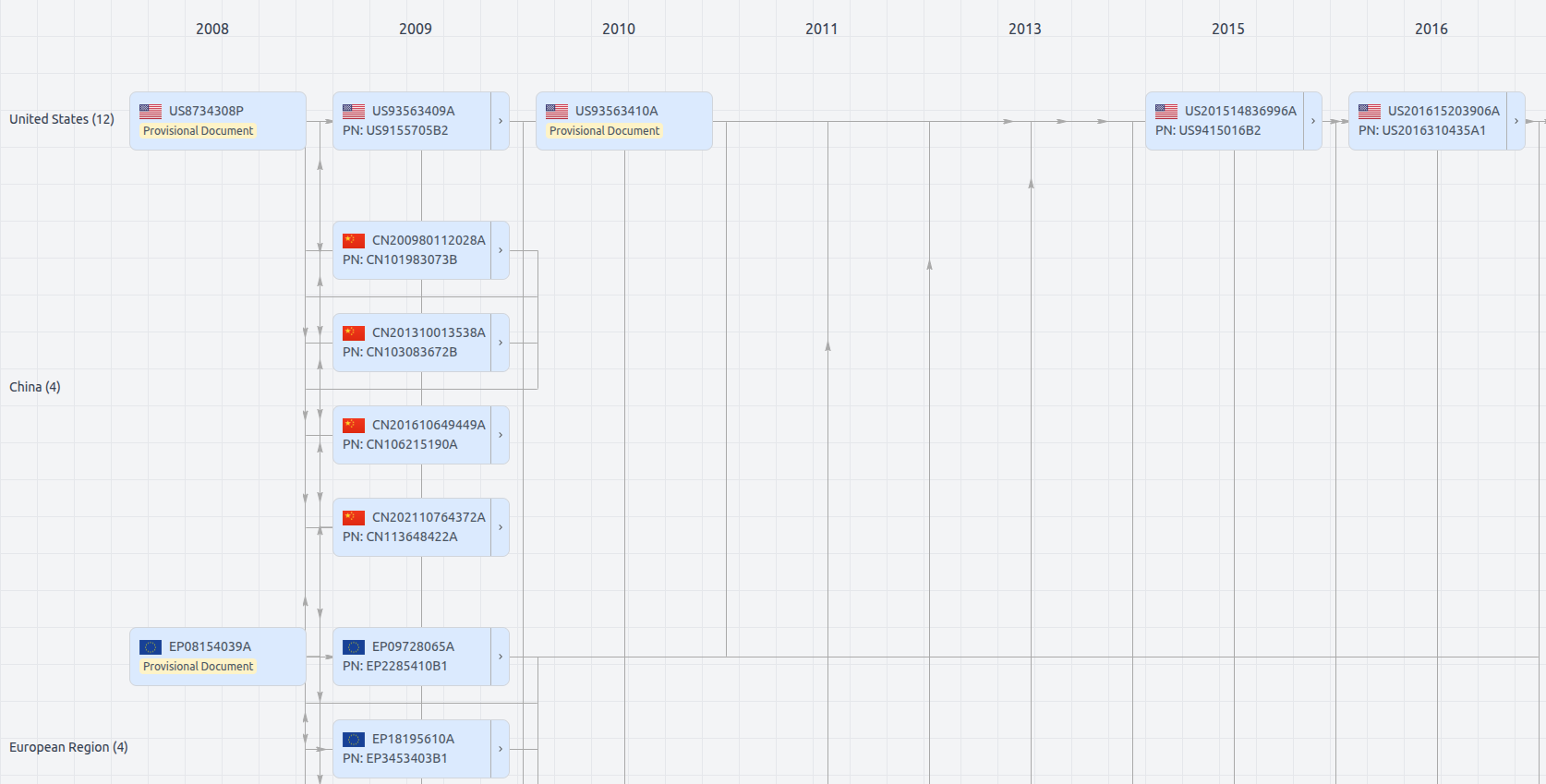
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11551743
- Application Number
- US16940858
- Filing Date
- Jul 28, 2020
- Status
- Expired
- Expiry Date
- Aug 20, 2024
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents