System And Method For Adapting A Neural Network Model On A Hardware Platform
Patent No. US11610117 (titled "System And Method For Adapting A Neural Network Model On A Hardware Platform") was filed by Tesla Inc on Dec 27, 2019.
What is this patent about?
’117 is related to the field of machine learning, specifically the adaptation and configuration of neural networks for deployment on various hardware platforms. The background acknowledges the increasing reliance on neural networks for tasks like image labeling and the challenges of implementing them on diverse platforms with varying resource constraints. Existing manual methods for configuring neural networks are time-consuming and require deep expertise, especially when considering the numerous decision points and constraints involved.
The underlying idea behind ’117 is to automate the process of adapting a neural network to a specific hardware platform by formulating the configuration problem as a constraint satisfaction problem . This involves identifying key decision points within the neural network architecture, such as data layout and algorithm selection, and then defining constraints based on the target hardware's capabilities and performance requirements. A satisfiability solver is then used to find a valid configuration that meets all the specified constraints.
The claims of ’117 focus on a method, system, and storage medium for adapting a neural network model to a hardware platform. The core steps involve obtaining neural network model information with decision points (including layout), accessing hardware platform information, determining constraints based on platform resources and performance metrics, and generating a candidate configuration using a satisfiability solver . The claims further specify updating the constraints to exclude the initial candidate configuration and generating additional configurations based on these updated constraints.
In practice, the system first analyzes the neural network model to identify configuration variables at each layer, such as the data type, layout, and algorithm to use. It then gathers information about the target hardware platform, including its processing capabilities, memory limitations, and supported instruction sets. Based on this information, the system defines constraints that must be satisfied for the neural network to run efficiently and correctly on the hardware. The satisfiability solver then explores the space of possible configurations, guided by these constraints, to find a valid solution.
’117 differentiates itself from prior approaches by automating the configuration process using a constraint satisfaction solver. Instead of relying on manual exploration and expert knowledge, the system systematically searches for valid configurations that meet the specific requirements of the hardware platform. By iteratively generating and excluding candidate configurations, the system can explore a wider range of options and potentially find more optimized configurations that maximize performance and resource utilization. This approach addresses the complexity of neural network deployment and reduces the burden on developers.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2010s when ’117 was filed, neural networks were being deployed across a wide range of platforms, at a time when developers commonly faced challenges in adapting models to specific hardware constraints. Satisfying performance metrics such as processing resource usage and evaluation time was typically non-trivial, requiring manual exploration of numerous configuration options and deep understanding of both the neural network architecture and the target platform's capabilities.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner allowed the claims because the prior art failed to teach or disclose obtaining neural network model information comprising a plurality of decision points associated with a neural network, wherein one or more first decision points are associated with a layout of the neural network; accessing platform information associated with a hardware platform for which the neural network model information is to be adapted; determining, based on the platform information, constraints associated with adapting the neural network model information to the hardware platform, wherein a first constraint is associated with a processing resource of the hardware platform and wherein a second constraint is associated with a performance metric; and generating a candidate configuration for the neural network via execution of a satisfiability solver based on the constraints, wherein the candidate configuration assigns values to the plurality of decision points, wherein the determined constraints are updated to include the candidate configuration as a negation, and wherein one or more other candidate configurations are generated based on the updated constraints, as claimed.
Claims
This patent contains 19 claims, of which claims 1, 11, and 17 are independent. The independent claims are directed to a method, a system, and a non-transitory computer storage medium, respectively, all generally focused on adapting neural network model information to a hardware platform using a satisfiability solver. The dependent claims generally elaborate on specific aspects, features, and functionalities of the method, system, or storage medium described in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
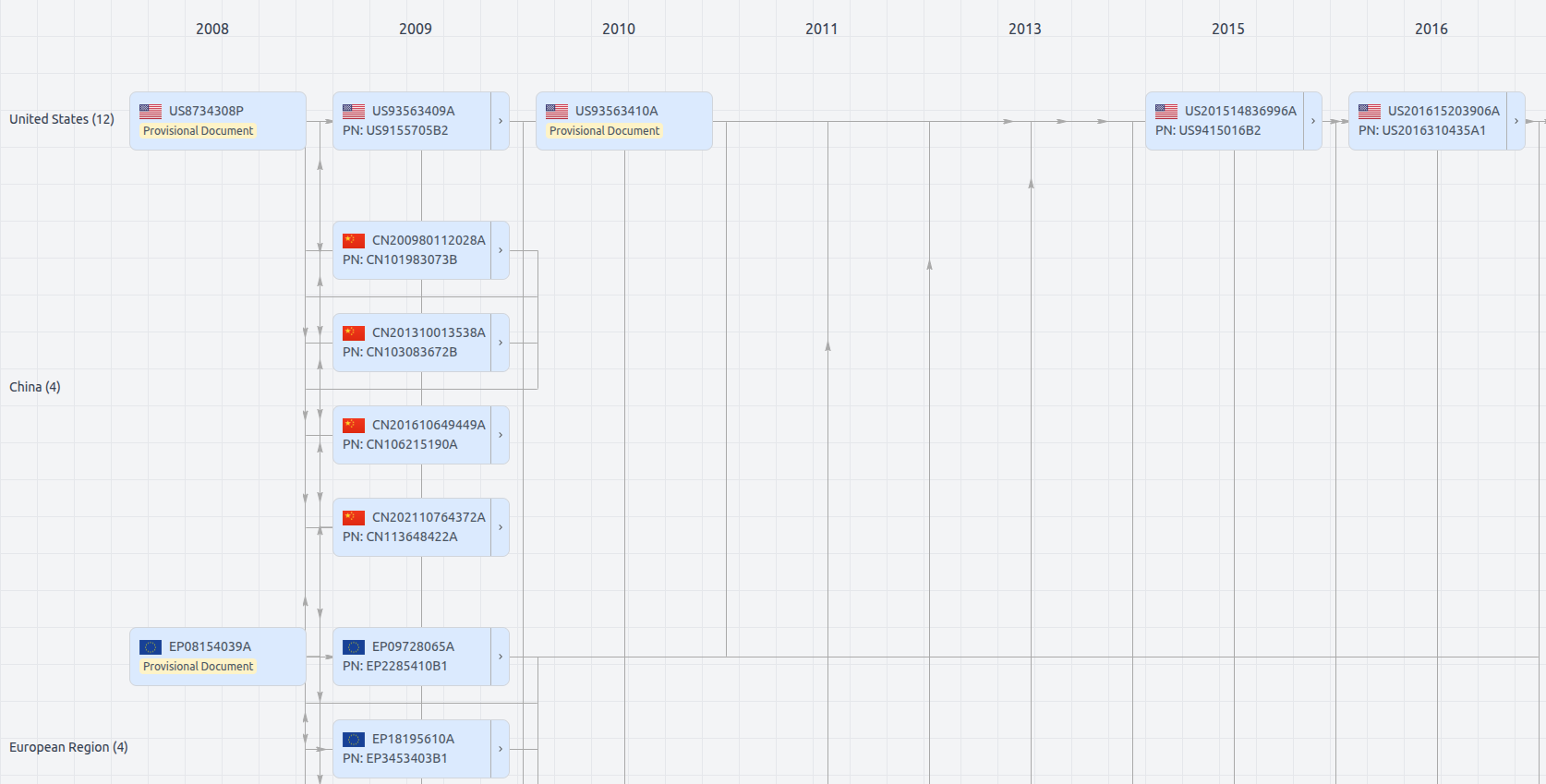
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11610117
- Application Number
- US16728884
- Filing Date
- Dec 27, 2019
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Mar 1, 2041
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents