Header Repetition In Packet-Based Ofdm Systems
Patent No. US11777776 (titled "Header Repetition In Packet-Based Ofdm Systems") was filed by Ax Wireless Llc on Sep 7, 2022.
What is this patent about?
’776 is related to the field of wireless communication systems, specifically addressing the problem of reliable header decoding in Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems. In OFDM, data is transmitted over multiple subcarriers, and each packet typically includes a header containing crucial control information. Ensuring the header is decoded correctly is vital for proper payload decoding and virtual carrier sensing, especially in noisy environments or when dealing with varying channel conditions.
The underlying idea behind ’776 is to improve header reliability by selectively repeating the header information across multiple OFDM symbols. Instead of always using a fixed number of symbols for the header, the system can dynamically choose to repeat the header, effectively increasing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for the header information. This header repetition provides diversity, making the header more robust against errors caused by channel impairments.
The claims of ’776 focus on a wireless communication device and method that can distinguish between two packet formats: one with a single header field in one OFDM symbol, and another with the same header field repeated in a subsequent OFDM symbol. The key is the ability to detect the repeated header field to identify the second packet format, thereby enabling more robust header decoding.
In practice, a receiver implementing this invention would first attempt to decode the header from the initial OFDM symbol. If the decoding fails, the receiver would then look for a repeated header in the following OFDM symbol. The presence of a matching header confirms the second packet format and allows the receiver to combine the information from both symbols to improve decoding accuracy. This approach allows for adaptive header robustness based on channel conditions.
This method differentiates itself from prior approaches that use a fixed number of OFDM symbols for the header, regardless of channel conditions. By dynamically adjusting the header repetition, the system can optimize the trade-off between overhead and reliability. Wideband devices operating in less noisy environments can use the single-header format, while narrowband devices or those experiencing poor channel conditions can benefit from the increased robustness of the repeated header format. This dynamic adaptation improves overall system efficiency and reliability.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2000s when ’776 was filed, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) was commonly used in multi-user communication systems. At a time when these systems typically relied on frame-based transmission with preambles, headers, and payloads, reliable header decoding was essential. When hardware or software constraints made it non-trivial to efficiently handle varying levels of frequency diversity across different bandplans, systems commonly relied on fixed header repetition schemes.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because the prior art of record failed to disclose a first packet format with a first header field, and a second packet format including both the first header field and a second header field, where the second header field is a repetition of the first. The examiner stated that claims 1-12 were allowable because, considering all limitations, they did not appear to be anticipated or obvious in view of the prior art.
Claims
This patent contains 12 claims, with independent claims 1 and 7. Claim 1 focuses on a wireless communication device that distinguishes between packet formats based on header field repetition, while claim 7 focuses on a corresponding wireless communication method. The dependent claims elaborate on the specifics of the device and method, such as network usage and header field content.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
Patent Family
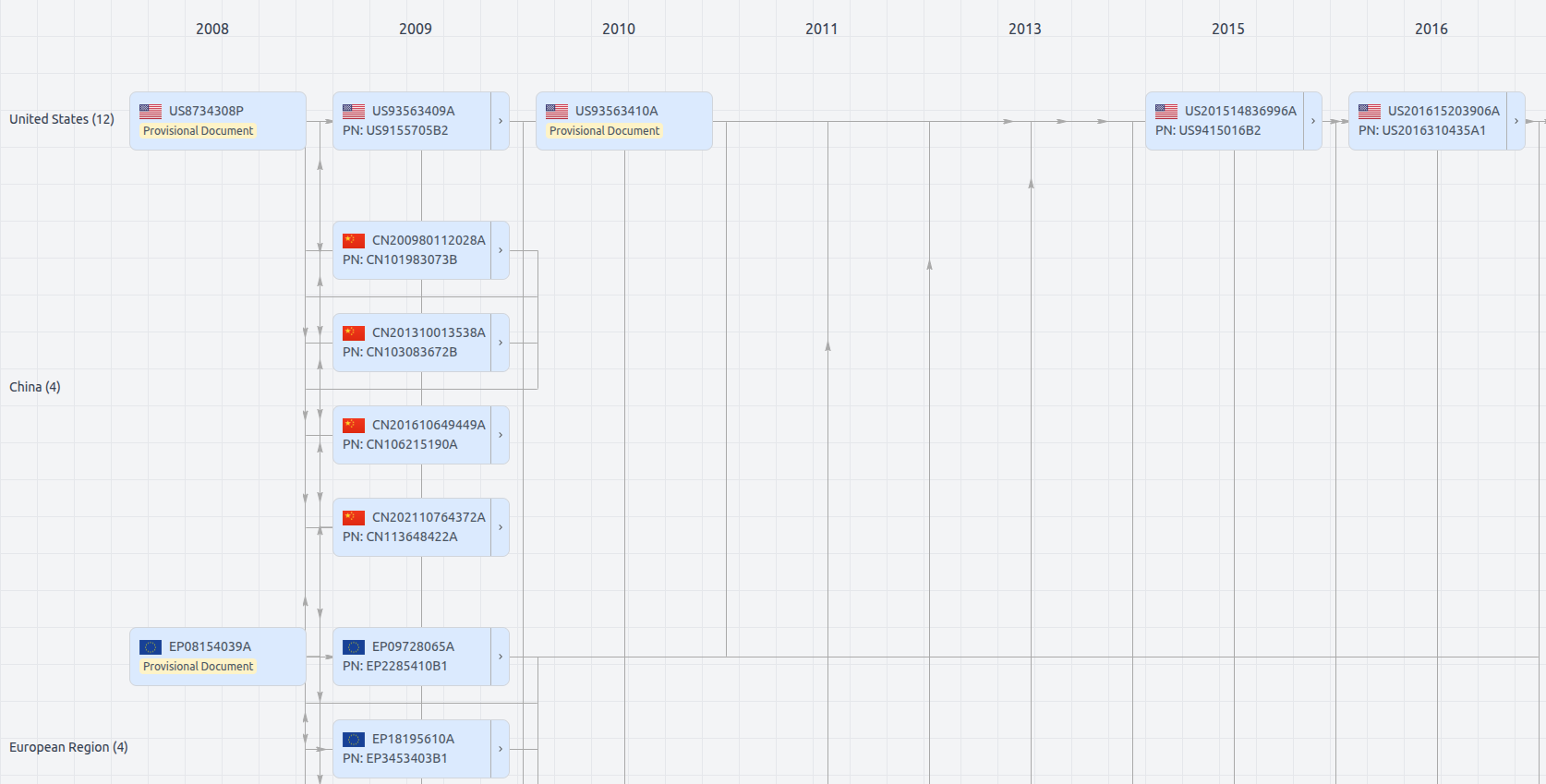
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11777776
- Application Number
- US17939904
- Filing Date
- Sep 7, 2022
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Aug 20, 2030
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents