Hybrid Arbitration System
Patent No. US11929073 (titled "Hybrid Arbitration System") was filed by Cerence Operating Co on Oct 3, 2022.
What is this patent about?
’073 is related to the field of automatic speech recognition (ASR) and, more specifically, to systems that arbitrate between speech recognition results generated locally on a device and remotely in the cloud. Modern voice interface systems often employ a hybrid approach, leveraging both on-device and cloud-based processing for ASR and natural language understanding (NLU). On-device processing benefits from access to personal user data, while cloud-based processing has greater computational resources.
The underlying idea behind ’073 is to intelligently select between a speech recognition result generated on a user's device and one generated by a cloud service, by using a two-stage arbitration process . The device first evaluates its own result using a "short-circuit" classifier. If the confidence in the local result is high enough, it's immediately selected, reducing latency. Otherwise, the system waits for the cloud result and then compares both results using a "system" classifier to choose the best one.
The claims of ’073 focus on a method, system, and software for selecting a speech recognition result on a computing device. The process involves acquiring speech data, soliciting recognition results from both the device and a cloud service, receiving the device's result and associated features, and then determining whether to immediately select the device's result or wait for the cloud's result . This determination is based on the device's result and its features, and the device's result is selected based on this determination.
In practice, the system uses deep neural networks (DNNs) as classifiers to estimate the confidence in each speech recognition result. The "short-circuit" classifier, which operates on the device's result alone, is trained to maximize the rate at which the device can confidently select its own result without waiting for the cloud. The "system" classifier, which compares both results, is trained to minimize word error rate by selecting the result with the highest accuracy. Features used by the classifiers include ASR confidence scores, NLU dialogue context, recognized domain/context/action names, entity names, and the top N-best word sequences.
This approach differentiates itself from prior solutions that rely solely on ASR confidence scores and application-specific heuristics. By incorporating a broader range of features, including NLU information and raw ASR strings, the system can capture more subtle context-specific differences between the on-device and cloud-based results. The use of DNNs allows for a more sophisticated and accurate assessment of the quality of each result, leading to a reduction in ASR errors and a faster response time for the user when the device can confidently select its own result.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2010s when ’073 was filed, hybrid automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language understanding (NLU) architectures were increasingly common in voice interface systems, at a time when on-device processing was typically constrained by limited computing resources, while cloud-based processing often lacked access to personal user data. This created a need for arbitration schemes to select between on-device and cloud-based results, when systems commonly relied on ASR confidence features and application-specific heuristics for this selection.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner allowed the claims because, although some claims taught similar subject matter to a prior art reference by Tang, the applicant addressed these concerns in their remarks filed on 10/24/2023 and a terminal disclaimer was filed. The dependent claims were considered allowable because they depended on an allowable base claim.
Claims
This patent contains 15 claims, with independent claims 1, 14, and 15. The independent claims focus on a method, system, and software, respectively, for selecting a speech recognition result on a computing device by comparing results from the device and a cloud service. The dependent claims generally elaborate on the features, steps, and conditions involved in the selection process described in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
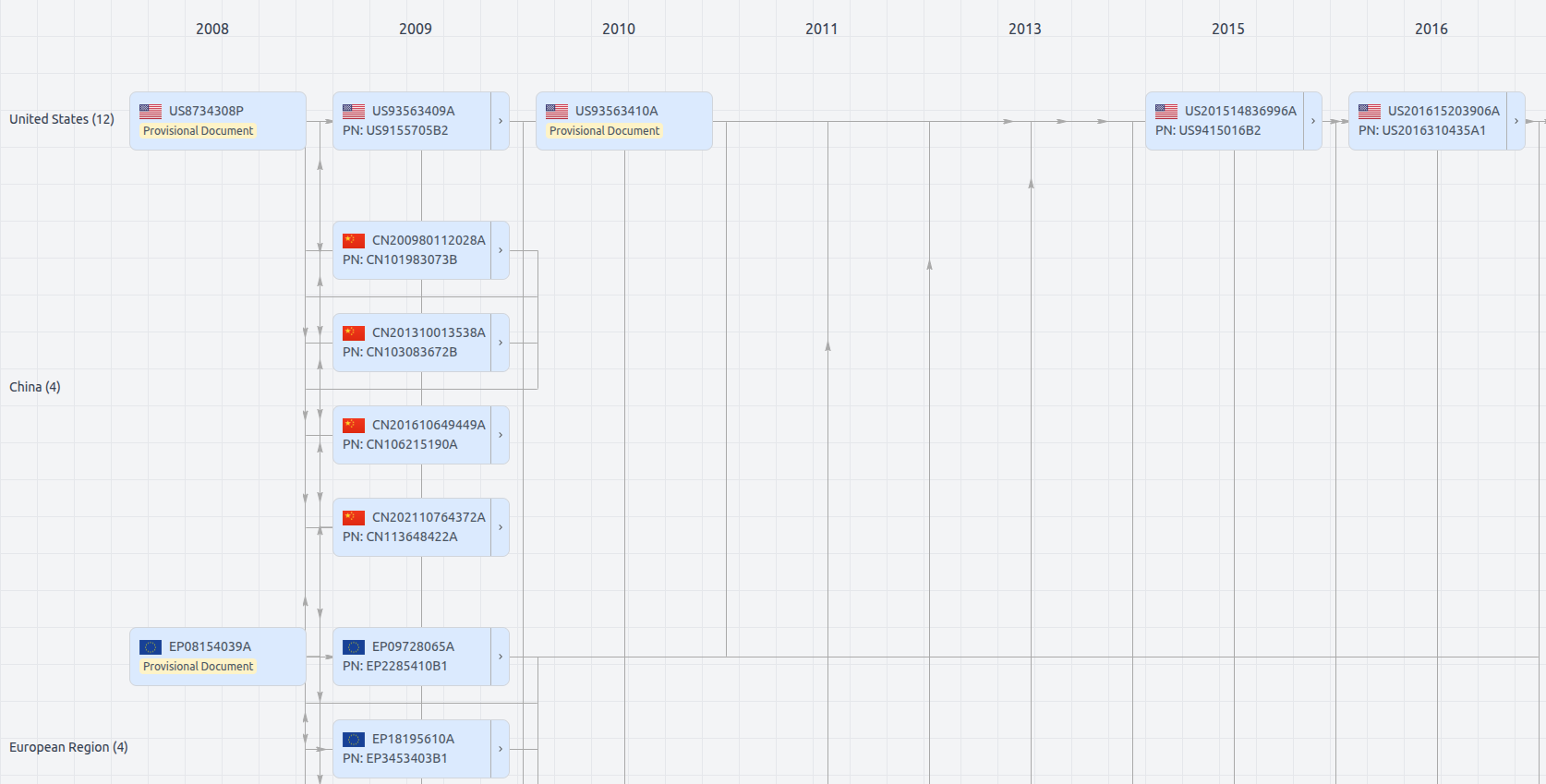
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US11929073
- Application Number
- US17958663
- Filing Date
- Oct 3, 2022
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Mar 26, 2040
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents