Selective Oxidation Of 5-Methylcytosine By Tet-Family Proteins
Patent No. US12018320 (titled "Selective Oxidation Of 5-Methylcytosine By Tet-Family Proteins") was filed by The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Department Of Health And Human Services on Feb 18, 2022.
What is this patent about?
’320 is related to the field of epigenetics, specifically to methods for regulating and detecting the cytosine methylation status of DNA. DNA methylation and demethylation are crucial in mammalian development, differentiation, aging, and tumorigenesis. Aberrant DNA methylation patterns are associated with various diseases, including cancer, making the ability to regulate and detect these modifications essential for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes.
The underlying idea behind ’320 is the discovery that the TET family of enzymes (TET1, TET2, TET3, and CXXC4) possesses a novel catalytic activity: the ability to convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) through hydroxylation. This conversion is significant because 5hmC has different binding properties than 5mC, potentially affecting gene expression and chromatin structure. The invention leverages this enzymatic activity for regulating and detecting DNA methylation.
The claims of ’320 focus on a method that involves providing a polynucleotide with an epigenetic modification, contacting it with a TET enzyme or its catalytic fragment, oxidizing the epigenetic modification to generate an oxidized form, and then using this oxidized form or a derivative to identify the original epigenetic modification. This method provides a means to detect and analyze DNA methylation patterns by exploiting the TET enzymes' ability to modify them.
In practice, the invention can be implemented by expressing or delivering TET enzymes to cells to alter their DNA methylation landscape. This can be used to reprogram somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells, improve stem cell therapies, or treat cancer by reactivating tumor suppressor genes silenced by methylation. The detection aspect can be implemented using antibodies or other binding agents that specifically recognize 5hmC or its derivatives, allowing for the mapping of DNA methylation patterns in various biological samples.
’320 differentiates itself from prior approaches by identifying the specific enzymatic activity of the TET family. Prior to this invention, the molecular mechanisms of active DNA demethylation were largely unknown. By identifying the hydroxylation of 5mC by TET enzymes as a key step, the invention provides a new target for therapeutic intervention and a new method for studying and manipulating epigenetic modifications. The use of the oxidized product, 5hmC, for identifying the original 5mC is also a novel approach, enabling more precise epigenetic analysis.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the late 2000s when ’320 was filed, DNA methylation and demethylation were recognized as vital processes in mammalian development, differentiation, aging, and tumorigenesis. At a time when active DNA demethylation mechanisms were not well understood at the molecular level, identifying molecules and methods to screen for changes in DNA methylation status was considered important for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because the claims were considered novel and non-obvious over the prior art. The claims were also enabled for their scope, as evidenced by the original disclosure. A terminal disclaimer was filed and accepted, ensuring that the patent's term would not extend beyond the expiration date of specified prior patents and a co-pending application.
Claims
This patent contains 13 claims, with claim 1 being the sole independent claim. Independent claim 1 is directed to a method of identifying an epigenetic modification of a polynucleotide by oxidizing the modification with an enzyme. The dependent claims generally specify or elaborate on elements of the method recited in claim 1, such as the source of the polynucleotide, the type of epigenetic modification, the method of identifying the oxidized modification, and the specific enzymes used.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
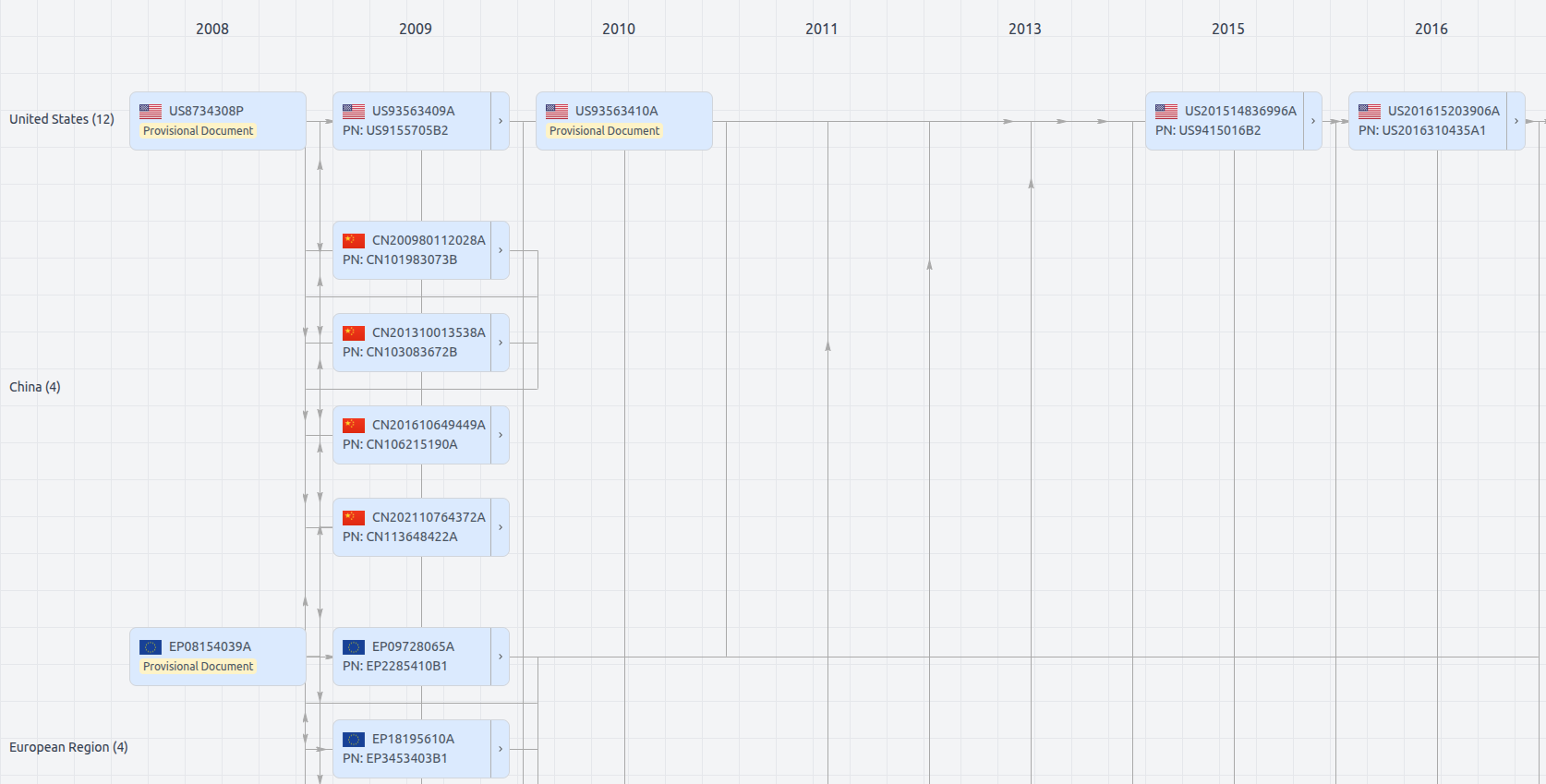
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US12018320
- Application Number
- US17675502
- Filing Date
- Feb 18, 2022
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Sep 28, 2029
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents