Three-Dimensional Memory Device And Method For Forming The Same
Patent No. US12075621 (titled "Three-Dimensional Memory Device And Method For Forming The Same") was filed by Yangtze Memory Technologies Co Ltd on Aug 27, 2021.
What is this patent about?
’621 is related to the field of three-dimensional (3D) NAND flash memory devices. These devices stack memory cells vertically to increase storage density, overcoming limitations of planar designs. Traditional 3D NAND structures involve complex fabrication processes to form vertical channels through stacked layers of conductive word lines and dielectric materials.
The underlying idea behind ’621 is to improve the reliability of 3D NAND flash memory by ensuring that the select gate transistors (either drain or source) function more like standard MOSFETs. This is achieved by physically separating the select gate from the memory film (charge trapping region) of the memory cell. Instead of the select gate dielectric contacting the memory film, it directly contacts the semiconductor channel itself.
The claims of ’621 focus on a 3D memory device comprising a doped semiconductor layer, a stack structure with interleaved conductive and dielectric layers, and a channel structure. The key feature is that either the drain select gate line (Claim 1) or the source select gate line (Claim 9) is in direct contact with the semiconductor channel of the channel structure, while the word lines are in direct contact with the memory film. Crucially, the select gate line and the word lines are made of the same material .
In practice, this is implemented by first creating the vertical channel structure with the semiconductor channel and surrounding memory film. Then, a portion of the memory film is etched away at the location of the select gate (either top or bottom), exposing the semiconductor channel. The select gate dielectric is then deposited directly onto the exposed channel. This ensures that the select gate transistor operates more predictably, preventing threshold voltage shifts that can occur when the select gate dielectric is adjacent to the charge trapping memory film.
This design differs from prior approaches where the select gate dielectric might be in contact with the memory film. By ensuring direct contact between the select gate dielectric and the semiconductor channel, the select gate transistor behaves more like a conventional MOSFET. This prevents unwanted threshold voltage shifts in the select gate transistor, improving the overall reliability and performance of the 3D NAND flash memory device. The use of the same material for the select gate and word lines simplifies manufacturing.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the early 2020s when ’621 was filed, 3D NAND flash memory was a well-established technology at a time when increasing memory density was typically achieved by vertically stacking memory cells. At that time, hybrid bonding techniques were commonly used for interconnecting stacked semiconductor wafers to create 3D memory devices. Forming high-density interconnects in 3D structures presented engineering challenges, especially when systems commonly relied on established fabrication processes.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because a prior art search did not reveal any references that disclosed or suggested the following limitations in combination: the drain select gate line being in direct contact with the semiconductor channel, each word line being in direct contact with the memory film, and the drain select gate line and word lines comprising the same material. The examiner also cited similar reasons for the allowability of claim 9, which depends on claim 1.
Claims
This patent contains 16 claims, with independent claims 1 and 9 directed to a three-dimensional (3D) memory device comprising a doped semiconductor layer, a stack structure, and a channel structure. The dependent claims generally elaborate on the specific materials, layers, and configurations of the 3D memory device described in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
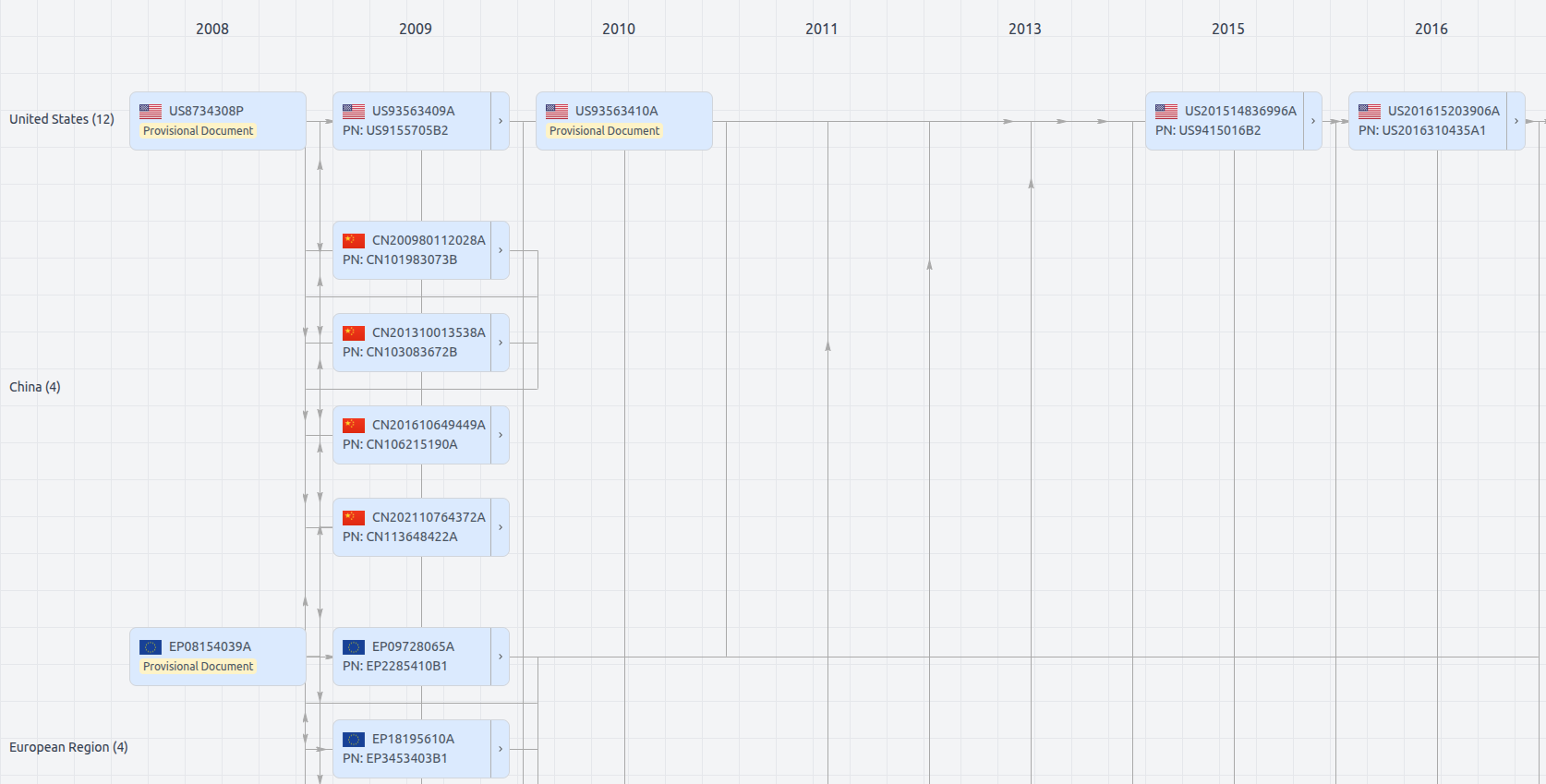
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US12075621
- Application Number
- US17459480
- Filing Date
- Aug 27, 2021
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Sep 17, 2042
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents