Methods For Neural Network-Based Voice Enhancement And Systems Thereof
Patent No. US12125496 (titled "Methods For Neural Network-Based Voice Enhancement And Systems Thereof") was filed by Sanas.Ai Inc on Apr 24, 2024.
What is this patent about?
’496 is related to the field of audio processing, specifically voice enhancement. Background noise and unclear speech (e.g., mumbling, slurring) can significantly degrade the quality and intelligibility of audio, hindering communication and the accuracy of speech recognition systems. Traditional voice enhancement techniques often focus on noise reduction, which can inadvertently distort speech features, leading to further inaccuracies. This patent addresses the need for improved voice enhancement that preserves speech characteristics while effectively suppressing noise and enhancing clarity.
The underlying idea behind ’496 is to use a two-stage neural network approach to enhance voice quality in real-time. The first neural network reduces the dimensionality of the input audio, focusing on relevant speech content and characteristics while discarding noise. The second neural network then reconstructs the audio from this reduced representation, generating enhanced speech that is clearer and more intelligible.
The claims of ’496 focus on a voice enhancement system, a method for real-time voice enhancement, and a non-transitory computer-readable medium. The independent claims cover the process of fragmenting input audio into frames, converting these frames into low-dimensional representations using a first neural network (which also removes non-content elements like noise), applying a second neural network to generate enhanced target speech frames, and combining these frames into output audio.
In practice, the system first takes an audio stream and divides it into short frames. The first neural network, having been trained on a large dataset of speech and noise, then transforms each frame into a compact, lower-dimensional representation. This representation is designed to capture the essential features of the speech while discarding irrelevant noise and artifacts. The second neural network then takes these compact representations and reconstructs them into enhanced speech frames, which are then stitched together to form the final output audio.
This approach differs from prior methods by explicitly using a low-dimensional representation to filter out noise and preserve speech characteristics. Instead of directly manipulating the raw audio signal, the system operates on a compressed representation, allowing it to more effectively separate speech from noise and enhance clarity. The two neural networks are trained to work together, with the first network learning to extract relevant features and the second network learning to reconstruct high-quality speech from these features.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the early 2020s when '496 was filed, voice enhancement was typically implemented using signal processing techniques in the STFT domain, often relying on ratio masks and equalization to reduce noise and improve speech clarity. At a time when systems commonly relied on noise reduction algorithms to preserve original speech audio, hardware or software constraints made it non-trivial to enhance speech intelligibility when the original speech was already degraded due to factors like slurring or mumbling.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The examiner approved the application because the prior art does not teach, disclose, or suggest applying a second neural network to the low-dimensional representations of input speech frames to generate target speech frames. This feature, in combination with all other claim limitations, distinguishes the invention from the prior art.
Claims
This patent contains 20 claims, with independent claims numbered 1, 11, and 16. The independent claims are generally directed to a voice enhancement system, a method for real-time voice enhancement, and a non-transitory computer-readable medium for voice enhancement, respectively, all involving neural networks to process and enhance audio data. The dependent claims generally elaborate on and refine the specifics of the voice enhancement system, method, and computer-readable medium described in the independent claims.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
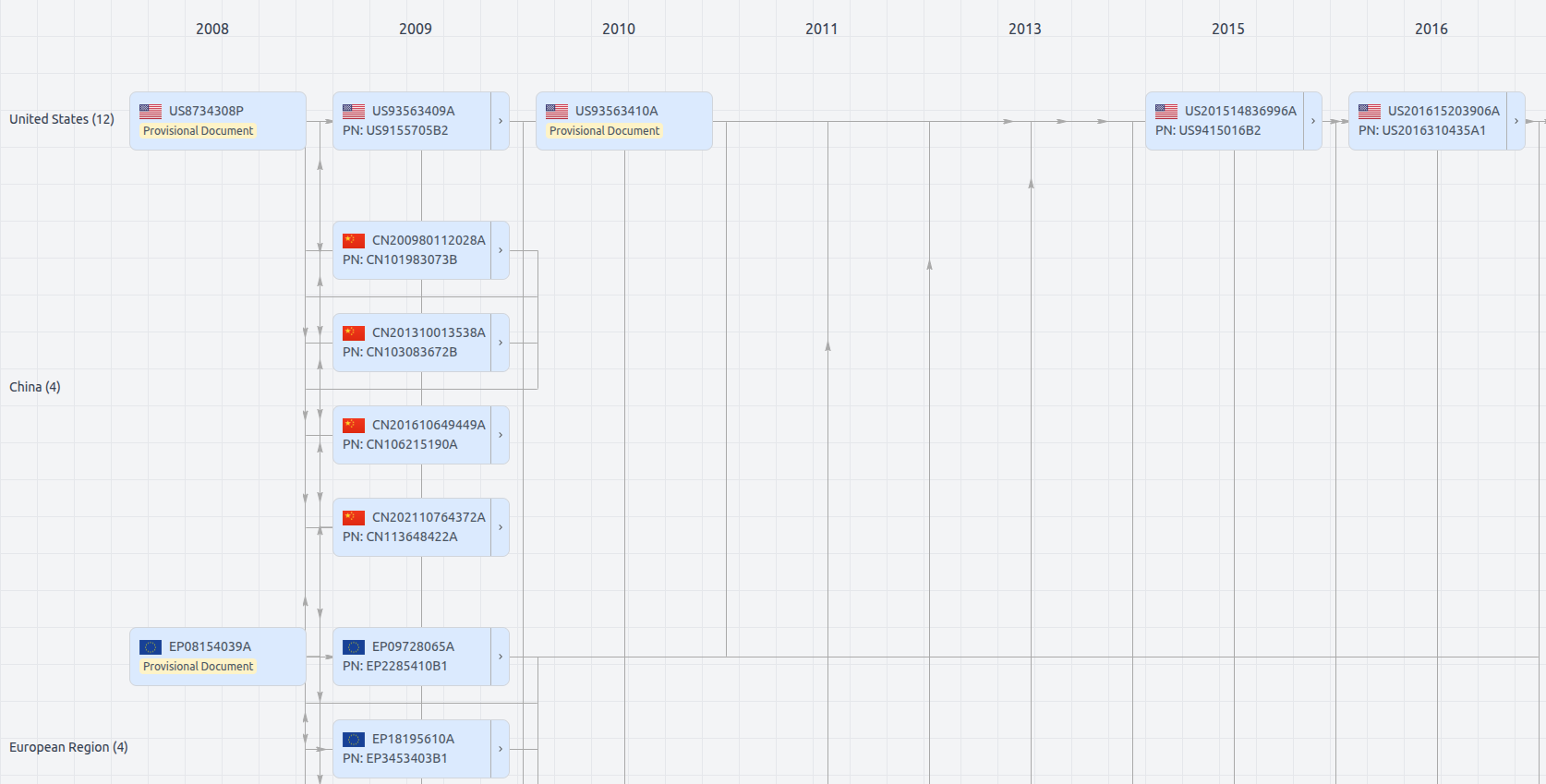
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US12125496
- Application Number
- US18644959
- Filing Date
- Apr 24, 2024
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Apr 24, 2044
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents