Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card Supporting Two-Factor Authentication
Patent No. US12207094 (titled "Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card Supporting Two-Factor Authentication") was filed by Nix John A on Jan 18, 2024.
What is this patent about?
’094 is related to the field of embedded universal integrated circuit cards (eUICCs) and their use in wireless communication systems. The background involves the increasing need for remote management of subscriber credentials in machine-to-machine (M2M) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, where physical SIM card swapping is impractical. Existing eUICC solutions face challenges in securely transferring network access credentials, particularly the pre-shared secret key K, without relying on potentially insecure third-party channels.
The underlying idea behind ’094 is to enhance the security of eUICC-based authentication by employing two-factor authentication and key derivation techniques . The system uses an initial, potentially less secure, connection to authenticate the device and user, then establishes a more secure connection using a derived key. This approach allows for remote key rotation and control over credential usage, even when the initial profile distribution is outside the mobile network operator's direct control.
The claims of ’094 focus on a method comprising generating a first message including an eUICC identity, a nonce, and a first digital signature using a first eUICC private key, sending the first message to a subscription manager system, deriving a second eUICC private key and a corresponding second eUICC public key using a first random number generator and a first set of cryptographic algorithms, storing a subscription manager public key, deriving a profile key using a key exchange algorithm, receiving from the subscription manager system, an encrypted profile comprising a ciphertext including a key K encrypted with a symmetric key, receiving the symmetric key, decrypting at least a portion of the encrypted profile using the profile key, decrypting at least a portion of the ciphertext using the symmetric key, and storing at least the key K in the embedded universal integrated circuit card for use in future communications.
In practice, the invention involves a module with an eUICC first connecting to a network and authenticating using initial credentials. After this initial authentication, the module and the mobile network operator (MNO) engage in a key exchange process, leveraging public-key cryptography and a key derivation algorithm. This process results in both the module and the MNO independently deriving a new shared secret key K, which is then used for subsequent, more secure communication.
This approach differentiates itself from prior solutions by avoiding the need to transmit the secret key K directly, even in encrypted form. Instead, the key is derived independently at both ends, enhancing security and reducing the risk of interception. Furthermore, the two-factor authentication ensures that only authorized users or devices can access the network, even if the initial profile distribution is compromised. This system also allows for periodic key rotation , further strengthening security over time without requiring physical intervention or complete profile replacement.
How does this patent fit in bigger picture?
Technical landscape at the time
In the early 2010s when ’094 was filed, wireless communication systems commonly relied on SIM cards and UICCs for authentication and network access. At a time when M2M communication was emerging, securely provisioning and managing these credentials, especially in remote or sealed devices, was non-trivial. The industry was beginning to explore eUICCs to address these challenges, at a time when standards were still in the requirements definition phase.
Novelty and Inventive Step
The application was rejected in a non-final office action. The claims were rejected under 35 U.S.C. 112(b) as indefinite and also for nonstatutory double patenting. The examiner indicated that the independent claim(s) 1 and their respective dependent claims are allowable if rewritten to overcome the rejections set forth in the office action. The prosecution record describes the examiner's reasoning for allowance.
Claims
This patent contains 22 claims, with claim 1 being the only independent claim. Independent claim 1 is directed to a method for securely provisioning an embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC) with a profile, involving key generation, encryption, and decryption steps. The dependent claims generally elaborate on and refine the method of independent claim 1, specifying details such as the source of the subscription manager public key, the type of key exchange algorithm used, the encryption method, authentication procedures, the type of module the eUICC is connected to, and the timing of certain steps.
Key Claim Terms New
Definitions of key terms used in the patent claims.
Litigation Cases New
US Latest litigation cases involving this patent.
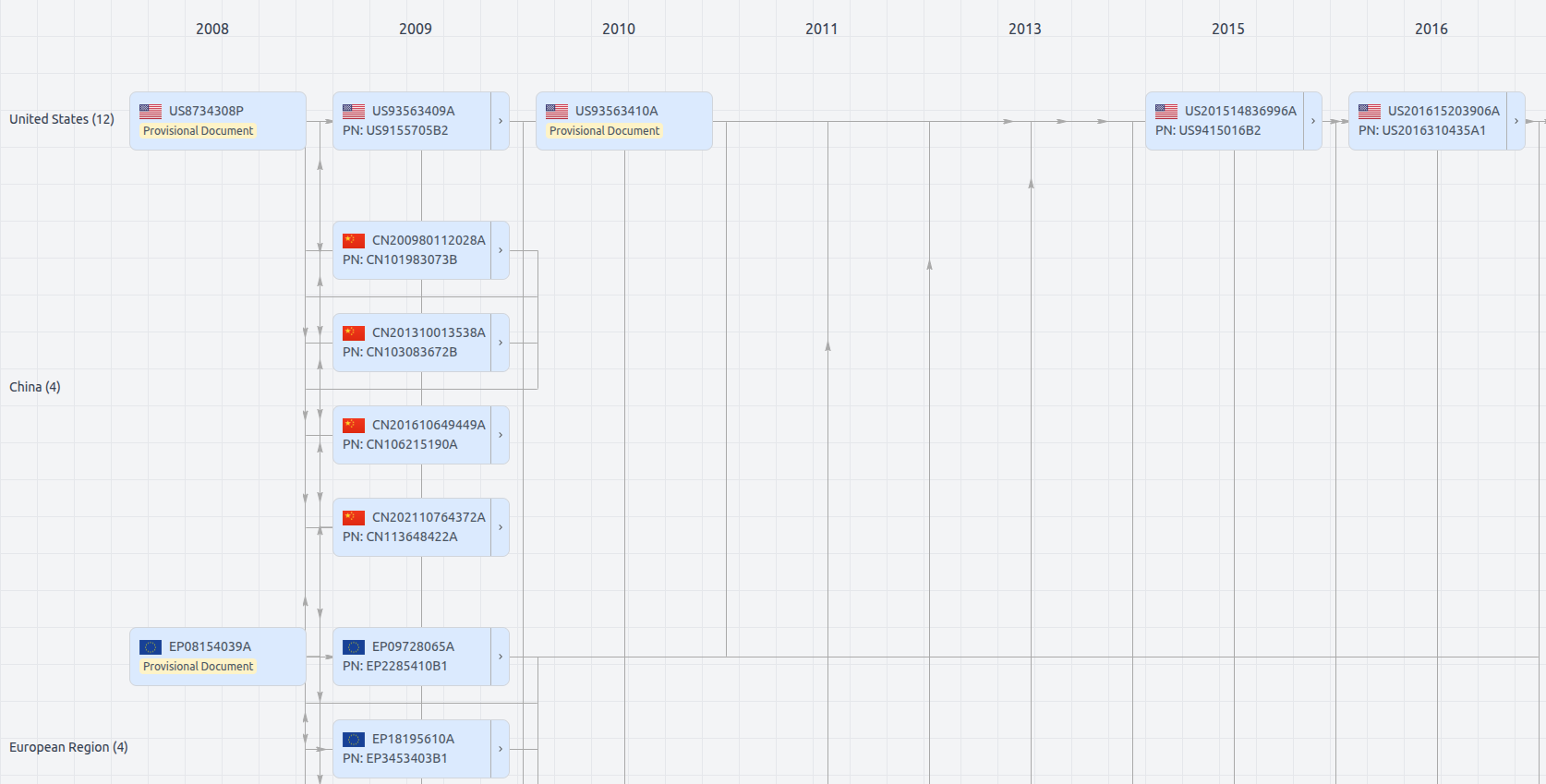
Patent Family
File Wrapper
The dossier documents provide a comprehensive record of the patent's prosecution history - including filings, correspondence, and decisions made by patent offices - and are crucial for understanding the patent's legal journey and any challenges it may have faced during examination.
Date
Description
Get instant alerts for new documents
US12207094
- Application Number
- US18416534
- Filing Date
- Jan 18, 2024
- Status
- Granted
- Expiry Date
- Dec 6, 2033
- External Links
- Slate, USPTO, Google Patents